Lifecycle rules
Lifecycle rules define a trigger and an action and can be applied to third parties and users.
Triggers are simple rules that define which objects should be processed by the lifecycle rule. Examples of trigger rules could be:
- All users with a start date of TODAY
- All users with a end date of TODAY
- All users with an end date of TODAY + 7 days
- All third parties with a contract end date of TODAY
In fact, any attribute of a third party or a user can be used to define a trigger, even All users with the first name of Oscar and a geographical location of United Kingdom who are currently ACTIVE. You are only limited by your imagination.
Actions, on the other hand, define what values should be assigned to specific attributes associated with the object that meets the criteria above.
To create a lifecycle rule, click on Add rule:

This will bring you to the add lifecycle rule page. Fill in the relevant details:
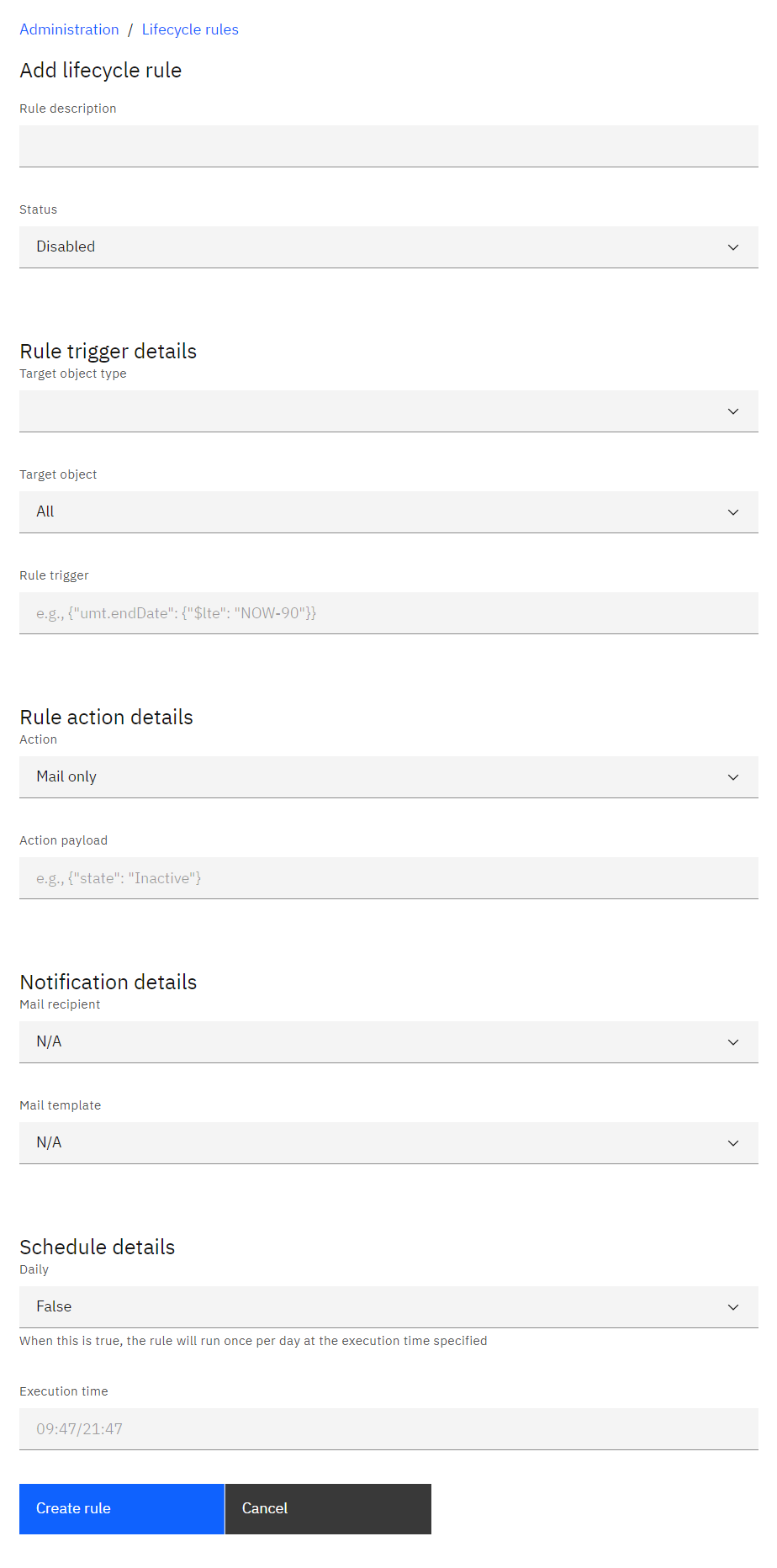
Lifecycle rule triggers
Triggers are formatted as JSON objects in the following format:
{ "attribute": "value" }They can have logic operators applied to them to trigger on specific criteria. Logic operators and ($and), or ($or) can be chained together within an array to target users that meet all criteria.
The below example targets users called John Doe:
{ "$and": [ { "givenName" : "John" } , { "familyName" : "Doe" } ] }The below example targets users called John or Jim:
{ "$or": [ { "givenName" : "John" } , { "givenName" : "Jim" } ] }Mathematical operators can also be used for triggers:
- $lt (less than)
- $lte (less than or equal to)
- $gt (greater than)
- $gt (greater than or equal to)
- $eq (equal to)
NOW is a special function that represents today's date. Days can be added to NOW as necessary. The following example targets users with an end date of 30 days from today:
{ "umt.endDate" : { "eq" : "NOW+30" } }Actions
Action payloads are also formatted as JSON objects although they do not have logical or mathematical operators applied to them. Instead, they simply state the attributes to be changed and what to change them to.
The below example sets a user's active status to false and their state to suspended:
{ "active" : false, "umt.state" : "Suspended" }Lifecycle rule attributes
|
Attributes |
Description |
|
Rule description |
A description of what the rule does. |
|
Status |
Whether the lifecycle rule should run or not. |
|
Target object type |
The type of object that the
rule will act upon: users, third parties, or one-time passcodes.
|
|
Target object |
Specifies whether the rule should act upon a specific user type or third party. |
|
Rule trigger |
Criteria to trigger the
lifecycle rule. |
|
Action |
Determines the outcome type of
the lifecycle rule. |
|
Action payload |
(For update actions only) The update that should be performed. |
|
Mail
recipient |
If selected, an email will be sent to the selected recipient
notifying them of the effects of the lifecycle rule. |
|
Mail template |
The mail template to be used for the
outgoing emails. |
|
Daily |
If enabled, the lifecycle will run every day at the specified time.
If not, then the rule will run every ten seconds. |
|
Execution time |
If the rule is set to run daily,
it will run at this time. Format must be 24-hour time as "HH:MM", e.g. 15:45. |